In India, a Registration Certificate (RC) is an essential document that legally binds a vehicle to its owner and verifies its roadworthiness. As per Section 39 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, no person can drive or allow a motor vehicle to be driven in a public place without a valid registration. This certificate, issued by the Regional Transport Office (RTO), is more than just proof of ownership—it connects a vehicle to the state’s transportation network.
In this blog, we’ll walk through what an RC entails, the types of RCs available (like digital and smart card versions), and the evolving technology, such as VAHAN, which has streamlined the registration process, and DigiLocker, which has made document storage and accessibility more efficient, secure, and convenient for both vehicle owners and authorities.
We’ll also discuss the various steps involved in obtaining a car registration certificate (RC), the importance of compliance, and how innovations are shaping the future of vehicle registration in India.
What is a Vehicle Registration Certificate (RC)?
A Car Registration Certificate (RC) assigns a unique identity to vehicles and links them legally to their owners. Governed by the Central Motor Vehicle Rules (CMVR), 1989, this process involves inspections to ensure safety and compliance with emissions standards. After fulfilling these requirements, the Regional Transport Office (RTO) issues the RC, which acts as proof of vehicle registration.
Additionally, digital tools like VAHAN enhance the registration process by enabling real-time data management, increasing transparency, and aligning with India’s digital governance objectives.
Information mentioned in an RC:
Owner’s full name, address, and contact details.
Vehicle specifications (make, model, engine number, chassis number, color).
Registration number and date of registration.
Validity of the registration and applicable road tax.
Hypothecation details, if applicable, with the associated bank.
Types of RCs in India
In India, automobile registrations are classified into numerous classes, each having a particular function. The RTO manages each form of registration, which has various criteria based on vehicle usage, ownership, and compliance.
Commercial Registration (Yellow Plate)
Vehicles used for commercial purposes, like taxis, trucks, and buses, are issued commercial registration with numberplates featuring black lettering on a yellow background.Temporary Registration (TR)
When a new vehicle is purchase, dealers issue a temporary registration, valid for a limited period (usually 180 days) until the permanent car registration is obtained.Permanent Registration (PR)
Issued by the RTO after a detailed vehicle inspection, with a validity of 15 years for personal vehicles and renewable every 5 years thereafter.
What is the significance of the RC?
The Registration Certificate (RC) is a vital document for both vehicle owners and government authorities in India, playing a critical role in multiple aspects of vehicle management and compliance.
Compliance with the law
In India, it is required by law for all vehicles driving on public roads to possess a valid registration certificate (RC). Operating a vehicle without a registration card can lead to penalties, seizures, or legal consequences.
Verification of ownership
The Registration Certificate is important for proving legal ownership when transferring ownership, selling the vehicle, or applying for loans or insurance claims.
Identification and safety of vehicles
In instances involving theft, accidents, or other legal issues, the RC serves as a dependable method for authorities to determine the vehicle and its owner.
You can read more about the Legal Framework for Vehicle Registration here.
Some of the Documents Required for Car Registration
- Form of Application (Form 20): Application for registration of a motor vehicle
- Proof of Address: Examples include Aadhaar card, voter ID, passport, or utility bills
- Identity Proof: Such as a PAN card, passport, or driving license
- Proof of Insurance: A valid motor vehicle insurance policy
- Sales Certificate (Form 21): Issued by the vehicle dealer
- Roadworthiness Certificate (Form 22): Provided by the manufacturer to certify compliance with safety and emission standards
- Temporary Registration Certificate: If applicable
- Pollution Under Control (PUC) Certificate: Required for vehicles that have been used, not mandatory for new vehicles
- Applicable Fees and Road Taxes: As specified by the local transport authority
Vehicle Registration Process in India
The vehicle registration process in India is meant to guarantee that all vehicles meet safety, insurance, and tax requirements before being driven on the roads. This process assigns a unique identity to each vehicle, linking it to the owner and validating it for roadworthiness and compliance with the law.
Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide on the vehicle registration process in India:
Step 1 Temporary Registration
When a new vehicle is purchased, the dealer provides a temporary registration to allow the owner to use the vehicle until permanent registration is completed. Valid for a limited period (usually 180 days).
Step 2 Document Submission to the RTO
To obtain a permanent car registration certificate, the owner must submit a set of documents to the RTO.
Step 3 Car Inspection by RTO
The RTO conducts a thorough physical inspection to verify the vehicle’s engine and chassis numbers and to ensure compliance with safety and emission standards. This inspection is a critical step to ensure that the vehicle is fit for road use.
Step 4 Payment of Fees and Road Tax
Registration fees, road tax, and any other applicable charges must be paid in full to complete the process.
Step 5 Permanent RC Issuance
Once all documents are verified and fees are paid, the RTO will issue a permanent care Registration Certificate (RC) for your vehicle. This RC may be provided as a smart card or a digital version accessible through apps like mParivahan and DigiLocker.
The document submission process typically takes about 15–20 days, after which the RC will be issued within 7–8 working days. Processing times may vary depending on the RTO’s workload and the accuracy of the submitted application.
Technological Developments in RC and Compliance
Significant advancements in technology have streamlined the car registration process and improved compliance with regulatory standards in India.
Here are some of the key developments that contribute significantly to efficient, transparent, and standardized car registration processes, aligning with India’s push towards digital transformation and road safety.
Digital Registration Certificates (Digital RC)
Accessible through platforms like mParivahan and DigiLocker, Digital RC allows vehicle owners to carry electronic versions of their car Registration Certificates, which are legally valid.
Advanced QR Codes on RC Smart Cards
New RC smart cards often feature advanced QR codes, which can be scanned for quick access to essential vehicle details like owner information, vehicle specifications, insurance, and emission status. This helps law enforcement quickly verify compliance without manually checking extensive paperwork.
Pollution Under Control (PUC) Digitization
PUC certificates are now digitally linked with the VAHAN database, making it easier to track and ensure that vehicles meet emissions standards. Real-time PUC data allows authorities to enforce emission standards more effectively and identify vehicles that fail to comply.
High-Security Registration Plates (HSRP)
The Indian government is implementing digital solutions and high-security registration plates (HSRPs) that provide increased security and ease of use for vehicle manufacturers and owners alike.
HSRP plates are made of reflective material for better visibility during night inspections, tamper-proof, and digitally linked to the vehicle’s registration data, ensuring easy verification by authorities. These plates are now mandatory for all vehicles in India.
Here’s our detailed guide on how to apply for the HSRP number plate.
Here’s how Shimnit helps to ensure a smooth car registration process:
RC Application Technology
Our unique RC Application Technology streamlines the vehicle registration process for car manufacturers (OEMs) and dealerships by facilitating data entry, document verification, and submission, resulting in increased operational efficiency.
Documentation & Compliance
Throughout the registration process, we provide expert guidance and help negotiate regulatory changes, resolve difficulties, and ensure that vehicle paperwork meets the essential criteria for successful registration.
Smooth updating using VAHAN
Shimnit helps update the RC application with the VAHAN system, allowing for real-time data management, error minimization, and faster registration.
So Shimnit’s RC applications send the required data to the Vahan portal, links HSRP to each owner’s Vehicle Registration Certificate (RC). The individual features or stored items of information are linked to the data in the registration system. Shimnit technology processes ensure all the below documents are linked together.
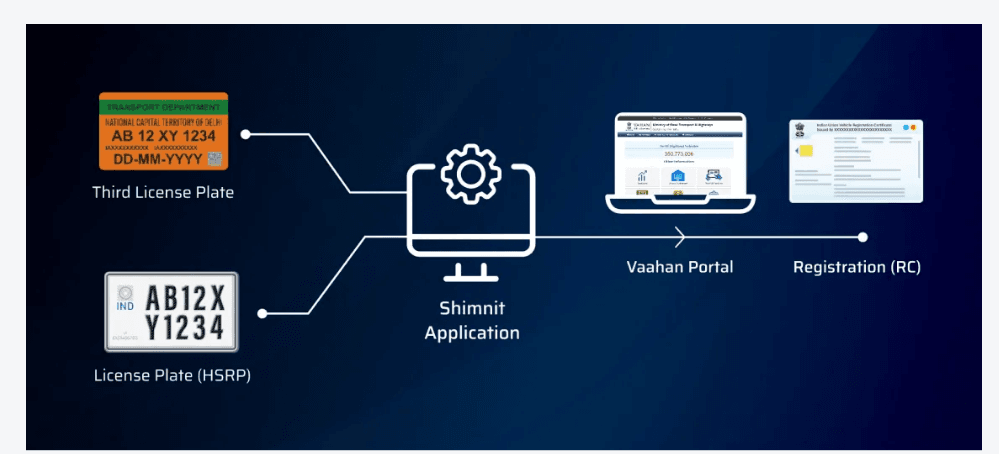
Conclusion
The Registration Certificate (RC) is a crucial component of car ownership in India since it provides legal recognition and allows for compliance with traffic laws. While the registration process might appear complex at times, technology improvements like digital RCs, e-governance platforms, and HSRPs are making it more accessible and safer.
As India transitions to a digital-first strategy, the future of car registration offers more efficiency and greater integration with national policy, paving the path for smoother, safer roads.






